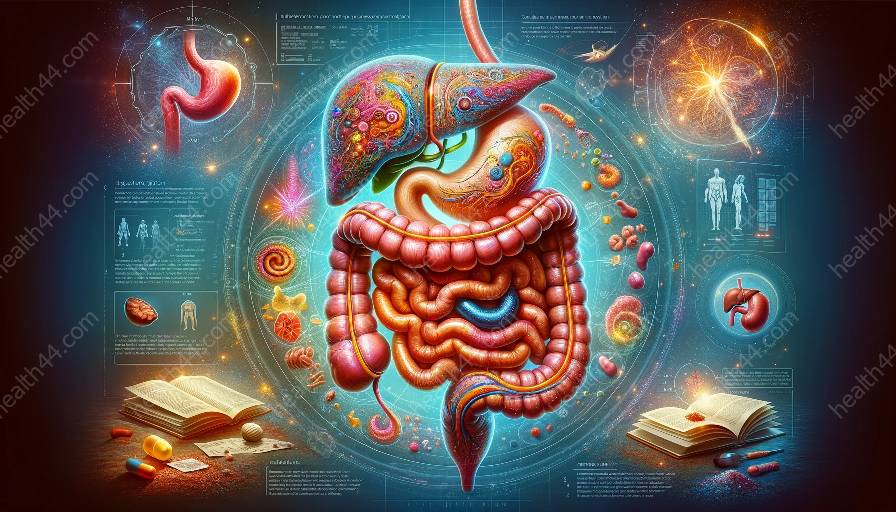
The human digestive system is an intricate network of organs and processes that work together to break down and absorb nutrients from the food we consume. Understanding its structure and function is essential for grasping the intricacies of human anatomy and physiology.
Anatomy of the Digestive System
The digestive system is composed of several key organs, each with its own distinct structure and function:
- Mouth: The digestive process begins in the mouth, where food is broken down mechanically by chewing and mixed with saliva, which contains digestive enzymes.
- Esophagus: This muscular tube carries food from the mouth to the stomach through a series of contractions known as peristalsis.
- Stomach: In the stomach, food is further broken down by stomach acid and digestive enzymes, forming a semi-liquid mixture known as chyme.
- Small Intestine: The small intestine is where the majority of nutrient absorption takes place. It is divided into three segments: the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum.
- Large Intestine: Also called the colon, the large intestine absorbs water and electrolytes from undigested food, forming feces.
- Liver: The liver produces bile, which aids in the digestion and absorption of fats.
- Gallbladder: The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile produced by the liver, releasing it into the small intestine as needed.
- Pancreas: The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes and produces insulin and glucagon to regulate blood sugar levels.
Function of the Digestive System
The digestive system performs several crucial functions in the body:
- Ingestion: The process of taking food into the body through the mouth.
- Digestion: The mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream.
- Absorption: The uptake of nutrients and water from the digestive tract into the bloodstream and lymphatic system.
- Compaction: The absorption of water and consolidation of indigestible waste into feces.
- Defecation: The elimination of feces from the body via the rectum and anus.
Importance of the Digestive System
The digestive system is vital for overall health and well-being. It plays a central role in providing the body with essential nutrients, energy, and hydration. Additionally, the digestive system is closely linked to the immune system and has a significant impact on overall immune function.
Understanding the structure and function of the digestive system can help individuals make informed choices about their diet and lifestyle, leading to better health outcomes and overall quality of life.