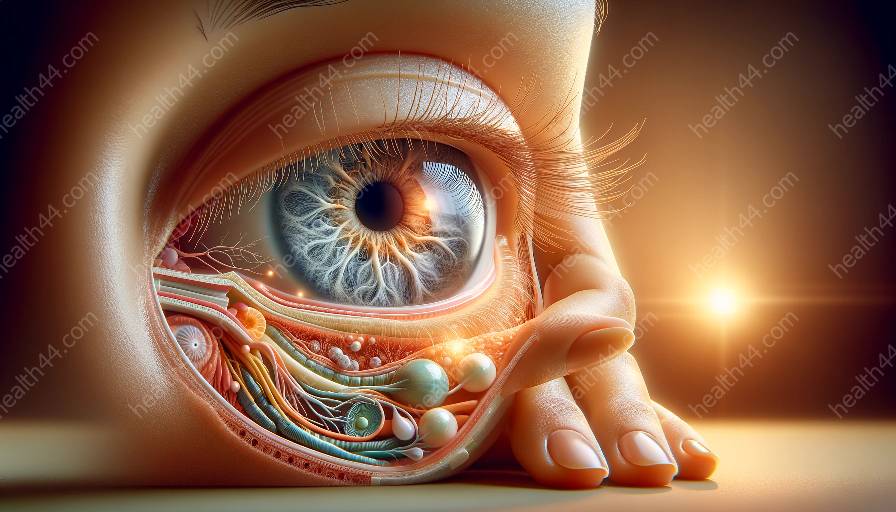
Providing adequate eye care in developing countries presents numerous challenges, impacting various aspects of eye health, including the pupil and the overall anatomy of the eye. This article will explore the multifaceted difficulties faced in delivering eye care, focusing on the implications for pupil and eye anatomy.
The Challenges
One of the major obstacles to providing eye care in developing countries is the lack of resources. Many of these nations struggle with insufficient funding, a scarcity of qualified eye care professionals, and a lack of access to basic facilities and equipment. This results in a significant gap in eye care services, leaving a large portion of the population without proper access to essential eye health services.
Additionally, there are cultural and social barriers that hinder the delivery of eye care in these regions. Myths and misconceptions about eye health, as well as traditional beliefs, often prevent individuals from seeking necessary medical attention, leading to a delay in diagnosis and treatment.
Furthermore, the prevalence of infectious diseases such as trachoma and onchocerciasis in developing countries contributes to the burden of eye care. These conditions, if left untreated, can lead to severe complications, including damage to the pupil and other structures within the eye.
Impact on Pupil and Eye Anatomy
The challenges in providing eye care have a direct impact on the health of the pupil and the anatomy of the eye. Lack of access to routine eye examinations and treatment for common conditions such as refractive errors can result in impaired vision, affecting the functionality of the pupil. Moreover, untreated eye infections and injuries can lead to complications that affect the overall anatomy of the eye, including the cornea, lens, and retina.
Furthermore, the lack of awareness and education about eye health contributes to a higher prevalence of preventable diseases, which can have lasting effects on the anatomy of the eye. For instance, conditions like cataracts, if left untreated, can cause irreversible damage to the lens and impact the pupil's ability to regulate the amount of light entering the eye.
Addressing the Challenges
Despite the complexities involved in providing eye care in developing countries, there are ongoing efforts to address these challenges. Initiatives focused on building sustainable eye care infrastructure, training local healthcare workers, and raising awareness about eye health have made significant strides in improving access to quality eye care services.
Collaborative partnerships between international organizations, governments, and local communities have also played a crucial role in addressing the challenges. By working together, these stakeholders have been able to implement comprehensive eye care programs, outreach activities, and advocacy campaigns to combat the obstacles hindering eye care delivery in developing countries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, delivering effective eye care in developing countries is a complex endeavor riddled with challenges. The impact on the pupil and eye anatomy is profound, as the lack of access to essential eye health services can result in vision impairment, damage to ocular structures, and a higher prevalence of preventable diseases. However, concerted efforts and initiatives aimed at addressing these challenges offer hope for improved eye care accessibility and outcomes in these regions.