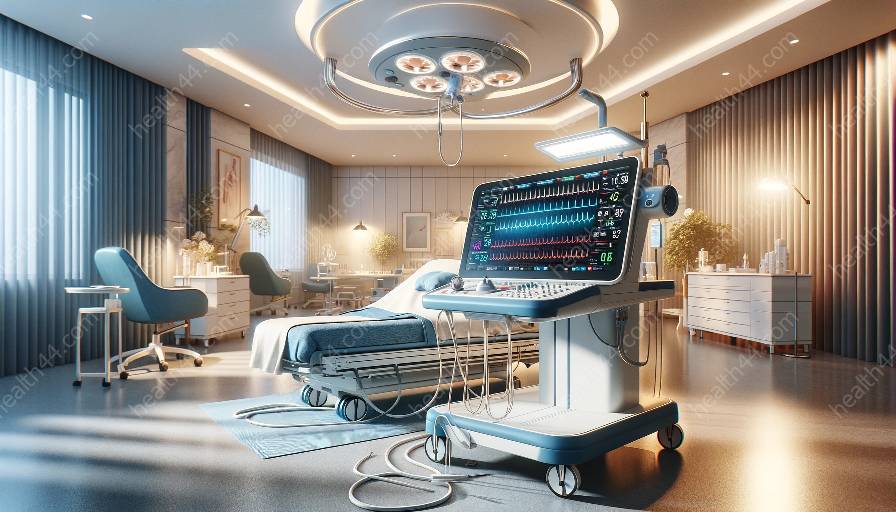
Medical devices and equipment play a crucial role in tracking and monitoring the impact of medications on heart function. In particular, electrocardiographs are vital tools used by healthcare professionals to assess the effects of various drugs on the heart's electrical activity and overall function.
Understanding Electrocardiographs
Electrocardiographs, commonly referred to as EKG or ECG machines, are devices that record the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time, typically a few seconds. This data is then used to diagnose various heart conditions and to monitor the effects of medications and treatments on the heart.
Assessing Cardiac Function
When patients are prescribed medications, especially those that may impact cardiac function, healthcare providers utilize electrocardiographs to closely monitor any changes in the heart's electrical activity. By examining the ECG readings before and after starting a new medication, healthcare professionals can assess whether the medication is affecting the heart's function, such as prolonging the QT interval, altering the rhythm, or affecting the overall conduction system.
Impact of Medications
Many medications have the potential to affect heart function, either directly or as a side effect. For example, certain antibiotics, antiarrhythmic drugs, and psychotropic medications can have an impact on the heart's electrical activity. Using an electrocardiograph to monitor the patient's ECG allows healthcare providers to identify any medication-related changes in heart function and take appropriate action.
Benefits of ECG Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of the heart's electrical activity through electrocardiographs offers several benefits when evaluating the impact of medications on heart function. ECG monitoring allows for early detection of any adverse effects on the heart, helps in adjusting medication dosages, and aids in making informed decisions regarding the continuation or discontinuation of specific drugs.
Advanced ECG Analysis
With advancements in technology, modern electrocardiographs are capable of providing detailed analysis of the heart's electrical activity. By utilizing algorithms and machine learning, these devices can identify subtle changes in the ECG waveform, enabling healthcare providers to detect any medication-related effects on the heart with greater accuracy and efficiency.
Integration with Healthcare Systems
Electrocardiographs are often integrated with electronic health record (EHR) systems, allowing for seamless storage and retrieval of ECG data. This integration facilitates comprehensive documentation of medication impact on heart function, enabling healthcare providers to track and analyze longitudinal changes in the patient's cardiac health over time.
Multidisciplinary Collaboration
Assessing the impact of medications on heart function requires collaboration among healthcare professionals from various specialties, including cardiology, pharmacy, and internal medicine. Electrocardiographs serve as a common tool that enables multidisciplinary teams to monitor and evaluate medication effects on the heart, leading to more coordinated and effective patient care.
Future Trends in ECG Technology
As the healthcare industry continues to advance, the role of electrocardiographs in assessing the impact of medications on heart function is likely to evolve. Innovations such as portable ECG devices, telemedicine integration, and enhanced connectivity are expected to further enhance the capabilities of ECG monitoring and its role in medication assessment.
Conclusion
The use of electrocardiographs in assessing the impact of medications on heart function is integral to ensuring patient safety and optimizing healthcare outcomes. By leveraging the capabilities of ECG technology, healthcare providers can effectively monitor, evaluate, and respond to medication-related effects on the heart, ultimately improving patient care and treatment strategies.