Chronic skin conditions can significantly impact a person's quality of life, often requiring advanced treatments for effective management. This comprehensive guide explores innovative approaches to treating chronic skin conditions, taking into account skin anatomy and general anatomy. By understanding the latest advancements and options available, individuals can make informed decisions to improve their skin health and overall well-being.
Skin Biology and Anatomy
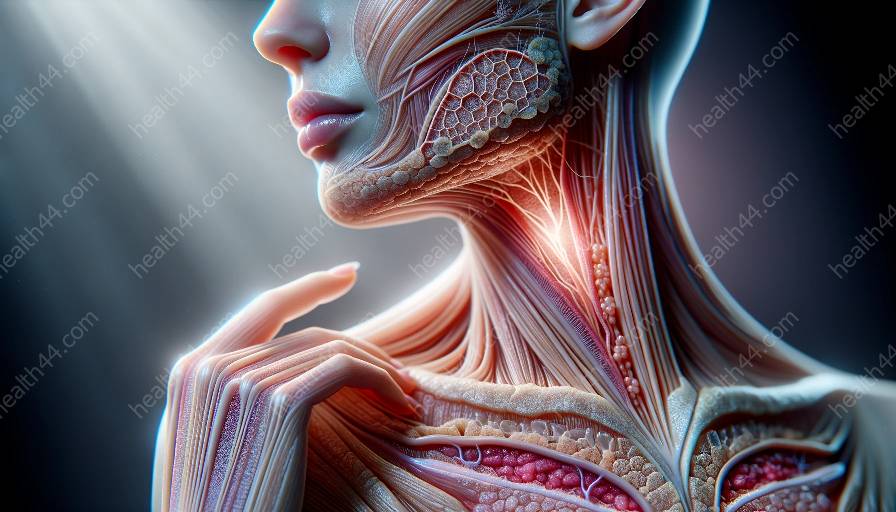
To understand innovative treatments for chronic skin conditions, it's essential to have a basic understanding of skin biology and anatomy. The skin is the largest organ in the human body, consisting of three primary layers: the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. Each layer serves unique functions and plays a crucial role in maintaining skin health.
Epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin and acts as a protective barrier against environmental factors, pathogens, and UV radiation. It also contains cells called keratinocytes, which produce the protein keratin, contributing to the skin's strength and flexibility. Additionally, the epidermis houses melanocytes, responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color and protects against UV damage.
Dermis
Beneath the epidermis lies the dermis, which contains blood vessels, nerve endings, hair follicles, and sweat glands. Collagen and elastin fibers in the dermis provide structural support and elasticity, helping the skin maintain its firmness and flexibility. The dermis also plays a crucial role in regulating body temperature and facilitating sensation.
Hypodermis
The hypodermis, or subcutaneous tissue, is the deepest layer of the skin and consists mainly of fat cells, blood vessels, and nerves. It acts as an insulating layer, helping to conserve body heat and providing cushioning and protection for the internal organs.
Common Chronic Skin Conditions
Chronic skin conditions encompass a wide range of disorders that affect the skin, often causing discomfort, pain, and psychological distress. Some of the most prevalent chronic skin conditions include eczema, psoriasis, acne, rosacea, and dermatitis. These conditions can be challenging to manage and may require ongoing treatment to control symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It often develops in childhood and can persist into adulthood, causing significant discomfort and impacting one's quality of life. While there is no cure for eczema, innovative treatments aim to reduce inflammation, relieve itching, and restore the skin's barrier function.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that leads to the rapid growth of skin cells, resulting in thick, scaly patches on the skin's surface. These patches, known as plaques, can be painful and may cause embarrassment or self-consciousness. Advanced treatments for psoriasis focus on slowing down the excessive skin cell production, reducing inflammation, and alleviating symptoms.
Acne
Acne is a common chronic skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. It can affect individuals of all ages and often has a significant impact on self-esteem and emotional well-being. Innovative treatments for acne target the underlying causes, such as excess sebum production, bacteria, and inflammation, to clear existing blemishes and prevent new breakouts.
Innovative Treatments
Advancements in dermatology and skincare have led to the development of innovative treatments for chronic skin conditions, offering new hope for individuals seeking effective solutions. These treatments utilize cutting-edge technology, scientific research, and a deep understanding of skin biology to address underlying issues and promote skin healing.
Biologics
Biologic medications, also known as biologics, are a revolutionary class of drugs designed to target specific components of the immune system involved in chronic skin conditions such as psoriasis and eczema. These medications are typically administered by injection or infusion and work by blocking the inflammatory pathways responsible for the development of skin lesions and symptoms.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy has emerged as a powerful tool in the treatment of chronic skin conditions, offering targeted and precise treatment options. Various types of lasers can be used to address different skin concerns, including pigmentation issues, vascular irregularities, and skin texture. Laser therapy can also stimulate collagen production and promote skin rejuvenation, leading to improved overall skin health.
Topical Immunomodulators
Topical immunomodulators are topical medications that target the immune system in the skin, effectively managing chronic conditions such as eczema. These medications help to reduce inflammation, relieve itching, and restore the skin's barrier function, offering a non-steroidal alternative for long-term eczema management.
Microbiome-based Therapies
The skin microbiome, consisting of various bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms, plays a critical role in maintaining skin health and immunity. Innovative therapies focused on modulating the skin microbiome aim to restore balance and diversity, ultimately supporting the skin's natural defense mechanisms and reducing the risk of chronic skin conditions.
Future Perspectives
As research and technology continue to advance, the future of innovative treatments for chronic skin conditions looks promising. More personalized and targeted approaches are expected to emerge, taking into account individual genetic predispositions, immune responses, and environmental triggers. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence, bioengineering, and regenerative medicine is likely to drive the development of revolutionary therapies with the potential to transform the landscape of dermatological care.
Personalized Medicine
With a deeper understanding of genetic factors and immune pathways contributing to chronic skin conditions, personalized medicine is poised to revolutionize treatment strategies. Tailored therapies based on an individual's unique genetic profile and immune response are anticipated to yield superior outcomes and minimize side effects, offering new hope for patients with challenging skin conditions.
Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine holds promise for addressing chronic skin conditions by harnessing the body's natural healing processes. Stem cell therapy, tissue engineering, and regenerative biologics offer potential solutions for repairing damaged skin, restoring functionality, and promoting long-term tissue regeneration. These approaches represent a paradigm shift in the treatment of chronic skin conditions, aiming to achieve true healing and functional restoration.
Artificial Intelligence in Dermatology
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in dermatology is set to revolutionize diagnostics, treatment planning, and outcome prediction. AI algorithms can analyze vast quantities of clinical data, imaging studies, and genetic information to identify patterns, predict disease progression, and optimize treatment recommendations. This intelligent integration of technology is expected to enhance precision and efficiency in managing chronic skin conditions.