Dental bridges are essential for restoring a natural-looking smile and maintaining proper oral function. Learning about the anatomy of teeth and understanding how dental bridges work is crucial for ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of the dental restoration. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the post-treatment care instructions for individuals with dental bridges, delve into the anatomy of the teeth, and discuss how to maintain optimal oral health with dental bridges.
Anatomy of the Teeth
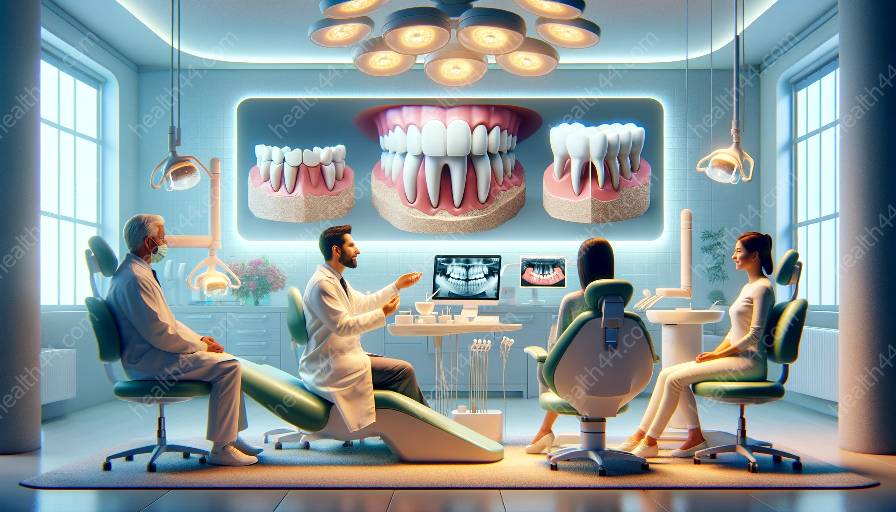
Before delving into post-treatment care for dental bridges, it is important to understand the anatomy of teeth. The human dentition comprises different types of teeth, each playing a crucial role in chewing, speaking, and maintaining facial aesthetics. The main types of teeth include incisors, canines, premolars, and molars.
Incisors are the front teeth used for cutting and chopping food. Canines, also known as cuspids, are sharp teeth used for tearing food. Premolars and molars are located in the back of the mouth and are responsible for grinding and crushing food during the chewing process.
The anatomy of a tooth consists of different parts, including the crown, enamel, dentin, pulp, and roots. The crown is the visible part of the tooth above the gum line, covered by enamel, which is the hardest substance in the human body. Beneath the enamel lies the dentin, a yellowish tissue that makes up most of the tooth structure.
The pulp is located at the center of the tooth and contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. The roots of the teeth anchor them in the jawbone and provide stability and support to the tooth structure.
Dental Bridges: Understanding the Basics
Dental bridges are a popular dental restoration used to replace missing teeth and restore proper oral function. A dental bridge consists of two main components: the abutment teeth and the pontic. The abutment teeth are the natural teeth or dental implants on either side of the gap left by the missing tooth or teeth. The pontic is the false tooth that fills the gap and is attached to the abutment teeth.
There are different types of dental bridges, including traditional bridges, cantilever bridges, and Maryland bonded bridges. Traditional bridges are the most common type and involve creating a crown for the teeth on either side of the missing tooth, with the pontic placed in between. Cantilever bridges are used when there are adjacent teeth on only one side of the missing tooth, while Maryland bonded bridges use metal or porcelain frameworks to attach the pontic to the back of the adjacent teeth.
Post-Treatment Care for Dental Bridges
After receiving dental bridges, proper post-treatment care is essential to ensure their longevity and maintain optimal oral health. Here are some important instructions for individuals with dental bridges:
- Oral Hygiene: Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for the long-term success of dental bridges. Brushing teeth at least twice a day, flossing between the abutment teeth, and using an antimicrobial mouth rinse can help prevent plaque buildup and protect the surrounding teeth and gums.
- Dietary Considerations: Individuals with dental bridges should be mindful of their dietary choices to avoid damaging the restoration. Avoiding hard and sticky foods, as well as excessive chewing on one side of the mouth, can help preserve the integrity of the dental bridges.
- Regular Dental Visits: Routine dental check-ups and professional cleanings are important for assessing the condition of the dental bridges and addressing any potential issues early on. Dentists can also provide guidance on proper oral care and maintenance of dental bridges.
- Protection during Physical Activities: Individuals with dental bridges should consider wearing a mouthguard during contact sports or activities that pose a risk of dental injury. Protecting the teeth and the dental restoration can help prevent damage and ensure the longevity of the bridges.
- Managing Oral Conditions: In case of any oral conditions or discomfort, individuals with dental bridges should seek professional dental care promptly. Addressing issues such as tooth sensitivity, gum inflammation, or loosening of the bridge components is essential for maintaining oral health.
Maintaining Optimal Oral Health with Dental Bridges
Proper post-treatment care and maintenance of dental bridges are vital for preserving oral health and the longevity of the restoration. By understanding the anatomy of teeth and the function of dental bridges, individuals can take proactive steps to ensure the success of their dental restoration. Adhering to the recommended post-treatment care instructions and seeking regular dental care can contribute to a healthy and functional smile.