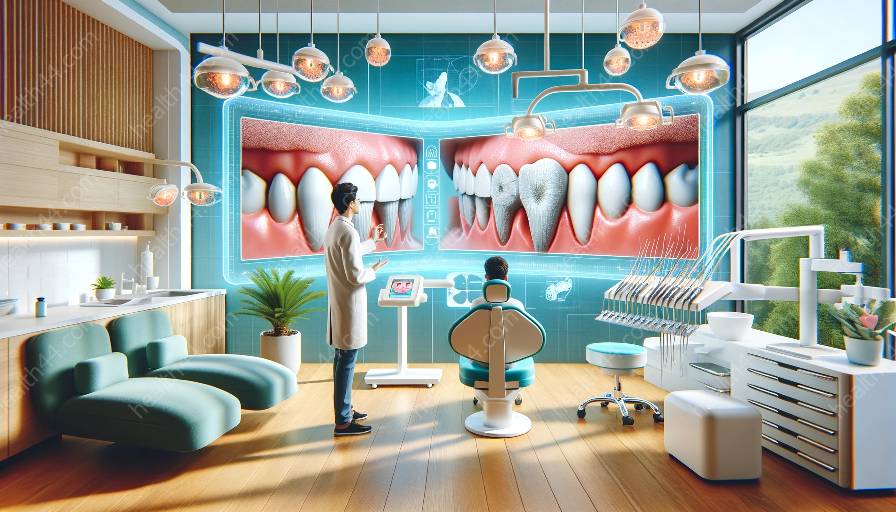
Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, is a serious condition that affects the gum tissues and supporting bones around the teeth. Left untreated, periodontal disease can lead to tooth loss and other systemic health issues. Gingivectomy is a surgical procedure that plays a crucial role in managing periodontal disease by removing and reshaping diseased gum tissue to promote healthier healing and prevent further damage.
Understanding Periodontal Disease and Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of periodontal disease, characterized by inflammation of the gums caused by the presence of plaque and bacteria. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which involves damage to the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth. Gingivectomy is often used as a treatment for advanced periodontal disease to remove diseased tissue and improve overall oral health.
The Role of Gingivectomy in Managing Periodontal Disease
Gingivectomy is a surgical procedure that targets and removes diseased gum tissue, allowing for better access and visibility of the teeth roots and supporting bone. This procedure is often recommended when non-surgical treatments, such as scaling and root planing, are ineffective in controlling periodontal disease. By removing the diseased tissue, gingivectomy creates an environment that is easier to clean, thus reducing the risk of bacterial growth and preventing further damage to the gums and bone.
One of the key roles of gingivectomy in managing periodontal disease is to promote gum tissue regeneration. Once the diseased tissue is removed, the body can begin the process of healing and regenerating healthier gum tissue. This promotes a tighter seal around the teeth, reducing the likelihood of reinfection and supporting overall periodontal health.
Benefits of Gingivectomy
There are several benefits of gingivectomy in managing periodontal disease, including:
- Targeted Removal of Diseased Tissue: Gingivectomy allows for precise removal of the areas affected by periodontal disease, creating a cleaner and healthier environment for the gums and teeth.
- Promotion of Healing: By removing diseased tissue, gingivectomy encourages the body's natural healing processes to regenerate healthier gum tissue, reducing the risk of further infection.
- Improved Access for Oral Hygiene: After gingivectomy, the gums are reshaped to provide easier access for thorough cleaning, making it easier to maintain good oral hygiene and prevent future plaque buildup.
- Prevention of Tooth Loss: By removing diseased tissue and promoting healing, gingivectomy can help prevent the progression of periodontal disease and reduce the risk of tooth loss.
Considerations for Gingivectomy
While gingivectomy offers many benefits, there are also considerations to take into account, including:
- Post-operative Care: Following a gingivectomy, it is important to follow specific post-operative instructions provided by the dental professional to promote proper healing and reduce the risk of complications.
- Candidacy: Not all patients with periodontal disease may be suitable candidates for gingivectomy. Factors such as overall oral health, medical history, and extent of periodontal disease will be taken into consideration.
- Adjunctive Treatments: In some cases, gingivectomy may be performed in conjunction with other periodontal treatments to achieve the best possible outcomes.
- Long-term Maintenance: Patients who undergo gingivectomy will need to maintain a good oral hygiene regimen and attend regular dental check-ups to prevent the recurrence of periodontal disease.
Conclusion
Gingivectomy plays a crucial role in managing periodontal disease by removing and reshaping diseased gum tissue and promoting healing and regeneration. By understanding the benefits and considerations of gingivectomy, patients can make informed decisions about their periodontal health and work with their dental professionals to achieve optimal outcomes.