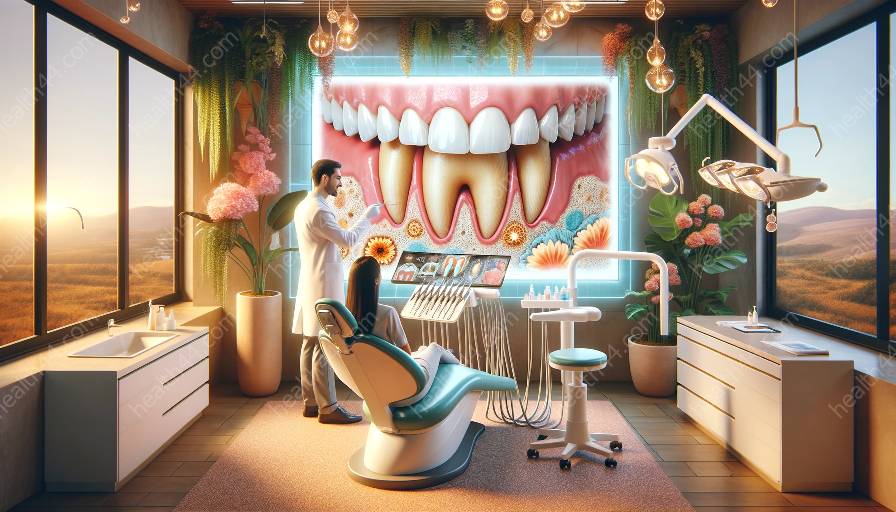
Dental plaque is a biofilm that forms on the teeth and is a significant contributor to oral health issues. Its accumulation can have a profound impact on oral health, and this impact can vary across different age groups. Understanding the age-related considerations in dental plaque accumulation is essential for maintaining good oral health throughout a lifetime.
Impact of Dental Plaque on Oral Health
Dental plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth and can lead to various oral health problems if not effectively managed. It is the primary cause of dental decay, gingivitis, and periodontal disease. When plaque accumulates and hardens into tartar, it can contribute to gum inflammation and, if left untreated, can lead to tooth loss. Additionally, the bacteria in dental plaque can produce acids that erode tooth enamel, leading to cavities.
Furthermore, dental plaque can contribute to bad breath, or halitosis, which can significantly impact an individual's social and psychological well-being. This underlines the importance of effective plaque management for overall oral health and quality of life.
Age-Related Considerations in Dental Plaque Accumulation
As individuals age, various factors can influence the accumulation of dental plaque and its impact on oral health. Understanding these age-related considerations is crucial for tailoring dental care to meet the specific needs of different age groups.
Children and Adolescents
In children and adolescents, the development of proper oral hygiene habits is essential to prevent dental plaque accumulation. This age group may be more susceptible to plaque accumulation due to dietary habits, irregular tooth brushing, and a lack of thorough oral hygiene practices. With guidance and education, children and adolescents can learn to effectively manage dental plaque, preventing the onset of oral health issues later in life.
Adults
Adults face challenges related to dental plaque accumulation due to lifestyle factors such as poor dietary choices, stress, and hormonal changes. Furthermore, as individuals age, changes in the oral cavity, such as reduced salivary flow and medications that can impact saliva composition, may contribute to increased plaque formation. Maintaining regular dental visits and adhering to a thorough oral hygiene routine can help mitigate these age-related factors contributing to plaque accumulation.
Seniors
For seniors, age-related factors can exacerbate dental plaque accumulation and its impact on oral health. Dry mouth, or xerostomia, is a common issue among seniors, often caused by medications and certain medical conditions. Reduced saliva flow can impair the natural cleansing and remineralization processes of the oral cavity, increasing susceptibility to dental plaque accumulation and associated oral health problems. Additionally, age-related changes in the gum tissue and tooth structure can contribute to an increased risk of plaque accumulation and subsequent oral health issues.
Management of Dental Plaque for Different Age Groups
Given the age-related considerations in dental plaque accumulation, tailored approaches to managing plaque are essential for different age groups. These approaches should encompass education, regular dental check-ups, and personalized oral hygiene routines to address the specific needs of each age group.
Children and Adolescents
Education and early intervention are key components of managing dental plaque accumulation in children and adolescents. Teaching proper tooth brushing techniques, encouraging a balanced diet, and promoting the use of fluoridated toothpaste are vital in preventing plaque build-up and supporting oral health. Additionally, regular dental check-ups can help identify and address any early signs of plaque-related issues.
Adults
For adults, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and stress management, can contribute to the prevention of dental plaque accumulation. Regular professional cleanings and check-ups are crucial for removing plaque and tartar buildup, as well as identifying and addressing any early stages of gum disease or tooth decay.
Seniors
Seniors require additional support in managing dental plaque accumulation, given the age-related challenges they face. Encouraging adequate hydration, using saliva substitutes as needed, and opting for oral hygiene products specifically designed for dry mouth can help alleviate the impact of reduced saliva flow. Regular dental visits, including screening for oral cancer, are essential for maintaining oral health in the senior population.
Conclusion
Dental plaque accumulation can have significant implications for oral health across different age groups. By understanding the age-related considerations and tailoring preventive measures and management strategies to meet the specific needs of each age group, it is possible to mitigate the impact of dental plaque and promote lifelong oral health. Education, regular dental care, and the adoption of personalized oral hygiene routines are key in addressing the challenges posed by dental plaque accumulation at every stage of life.