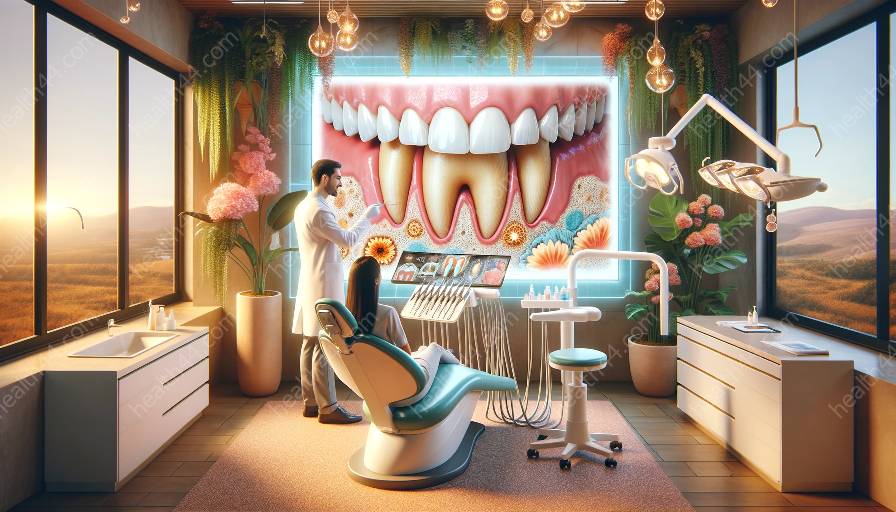
Dental plaque is a common problem that can lead to serious oral health issues. Understanding the impact of dental plaque on oral health, its causes, consequences, and prevention is essential for maintaining good dental hygiene. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the implications of dental plaque and potential serious dental health issues and provide valuable insights into its management and prevention.
Understanding Dental Plaque
Dental plaque is a sticky, colorless film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. It often develops at the gum line, between teeth, and on the chewing surfaces of the teeth. The bacteria in plaque thrive on sugars and starches from food, producing acids that can damage tooth enamel and lead to cavities and gum disease.
As plaque accumulates, it can harden and turn into tartar, which is more difficult to remove and requires professional dental cleaning. If left untreated, plaque and tartar buildup can lead to severe dental health issues, including:
- Tooth Decay
- Gum Disease
- Bad Breath
- Tooth Sensitivity
The Impact of Dental Plaque on Oral Health
Effects of dental plaque on oral health extend beyond just bad breath and yellow teeth. Plaque buildup can trigger a cascade of serious dental issues, such as tooth decay, gingivitis, and periodontitis. Understanding the impact of dental plaque on oral health helps individuals grasp the significance of maintaining effective oral hygiene practices.
Tooth Decay
Plaque produces acids that can erode tooth enamel, leading to cavities. If left unchecked, tooth decay can progress, causing significant damage to the teeth and eventual tooth loss.
Gum Disease
When plaque accumulates along the gumline, it can lead to inflammation and infection of the gums, known as gingivitis. If untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that can cause gum recession and even lead to tooth loss.
Bad Breath
The bacteria in plaque produce sulfur compounds that contribute to bad breath. Persistent bad breath, also known as halitosis, can be socially embarrassing and may signify underlying dental health issues.
Tooth Sensitivity
As plaque and tartar accumulate, they can cause exposure of the tooth roots, leading to increased tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, and sweet stimuli. Severe tooth sensitivity can disrupt daily activities and cause discomfort.
Preventing and Managing Dental Plaque
Effective oral hygiene practices are essential for preventing and managing dental plaque. Here are some crucial tips to combat dental plaque and maintain optimal oral health:
- Regular Brushing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste to remove plaque and prevent tooth decay.
- Flossing: Clean between your teeth daily with dental floss or interdental brushes to remove plaque from areas that a toothbrush can't reach.
- Mouthwash: Use an antiseptic mouthwash to reduce plaque and prevent gum disease.
- Regular Dental Visits: Schedule dental check-ups and professional cleanings at least twice a year to remove plaque and tartar buildup.
- Healthy Diet: Limit sugary and starchy foods that can contribute to plaque formation, and consume a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
- Quit Smoking: Avoid tobacco products, as smoking can contribute to plaque accumulation and increase the risk of gum disease.
By actively implementing these preventative measures, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of dental plaque and associated oral health issues, ultimately maintaining a healthy smile.