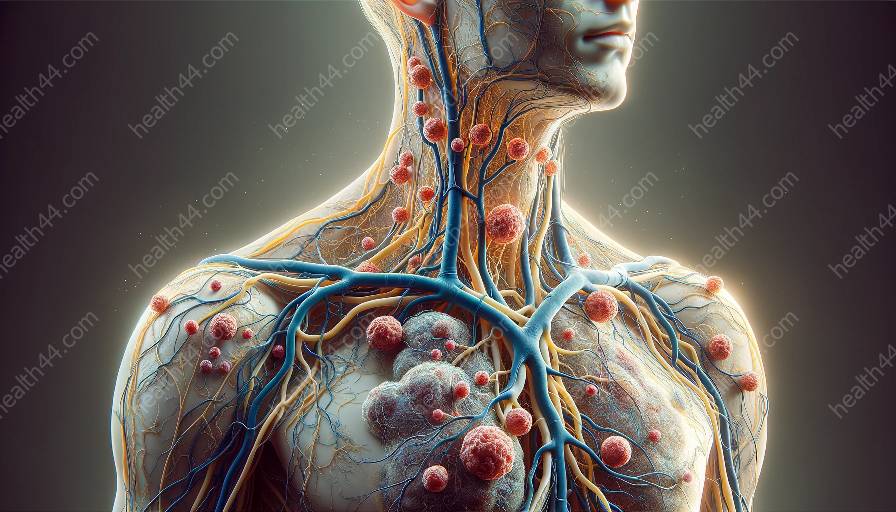
The lymphatic system plays a vital role in maintaining tissue homeostasis, working in coordination with the circulatory system to support immunity and fluid balance. Understanding the anatomy of the lymphatic system is crucial to appreciate its essential functions in the human body.
Overview of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is a network of vessels, tissues, and organs that help maintain fluid balance, support immune function, and facilitate the absorption of fats from the digestive system. Its primary components include lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, tonsils, spleen, and thymus gland.
Lymphatic Vessels and Capillaries
Lymphatic vessels, similar to blood vessels, form an extensive network that spans throughout the body. Lymphatic capillaries are thin-walled and highly permeable, allowing interstitial fluid, proteins, and cellular debris to enter the lymphatic system.
Role in Fluid Balance
The lymphatic system plays a pivotal role in maintaining tissue fluid balance by returning excess fluid from the interstitium back to the bloodstream. This process, known as lymphatic drainage, helps prevent tissue swelling and edema.
Immune Function
Lymph nodes are key structures within the lymphatic system where immune cells congregate and interact. They play a crucial role in filtering and trapping pathogens, antigens, and abnormal cells, allowing the immune system to mount an effective response against infections and diseases.
Role in Fat Absorption
Specialized lymphatic vessels called lacteals in the small intestine assist in the absorption of dietary fats and fat-soluble vitamins. These nutrients are transported via the lymphatic system before entering the bloodstream.
Lymphatic System and Tissue Homeostasis
The lymphatic system is intricately linked to maintaining tissue homeostasis by regulating fluid balance, facilitating immune responses, and aiding in nutrient absorption. Through its network of vessels and organs, the lymphatic system contributes to the overall health and function of tissues throughout the body.
Role in Waste Removal
In addition to maintaining fluid balance, the lymphatic system also aids in waste removal from tissues. Lymphatic vessels collect metabolic waste, toxins, and cellular debris, transporting them to lymph nodes for filtration and subsequent elimination from the body.
Importance of Lymphatic System in Anatomy
Understanding the lymphatic system is crucial in the study of human anatomy as it provides insights into how the body maintains internal equilibrium, defends against pathogens, and supports the transport of essential nutrients. An in-depth knowledge of the lymphatic system enhances the understanding of physiological processes and diseases related to lymphatic dysfunction.
Clinical Significance
Disorders affecting the lymphatic system, such as lymphedema and lymphoma, can have significant implications for overall health. Lymphatic drainage massage, compression therapy, and surgical interventions are among the approaches used to manage lymphatic disorders and maintain tissue homeostasis.