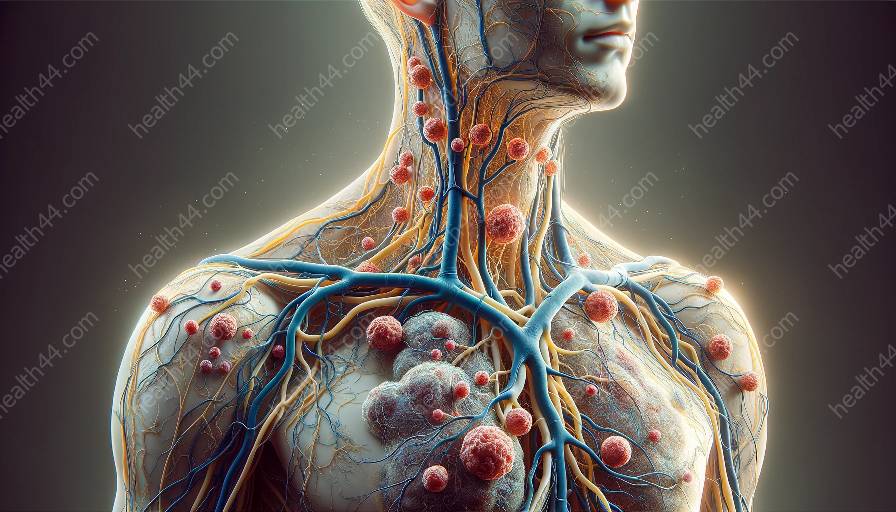
The lymphatic system is an essential part of the body's defense mechanism, working tirelessly to protect against pathogens and maintain overall health. This intricate network of vessels, nodes, and organs plays a pivotal role in immune response and the elimination of harmful invaders. By understanding the anatomy and functions of the lymphatic system, we can appreciate its remarkable contribution to preserving our well-being.
The Essential Components of the Lymphatic System
At the core of the lymphatic system are lymphatic vessels, which form an extensive network throughout the body, akin to blood vessels. These vessels work to transport lymph, a clear fluid containing white blood cells, proteins, and cellular debris, from tissues to the bloodstream. Lymph nodes, strategically positioned along the vessels, act as filtering stations, where harmful agents are trapped and destroyed by immune cells, such as lymphocytes and macrophages.
Additionally, the spleen, thymus, and tonsils represent key lymphoid organs that contribute to immune function. The spleen serves as a site for filtering blood and removing old or damaged blood cells, while the thymus is responsible for the maturation and selection of T-lymphocytes, crucial components of the immune system. Tonsils play a role in preventing the entry of pathogens through the oral and nasal cavities, serving as a first line of defense.
Role of the Lymphatic System in Pathogen Defense
When pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi, invade the body, the lymphatic system swiftly responds to neutralize the threat. Upon encountering pathogens, immune cells in the lymph nodes initiate an immune response by producing antibodies and activating T-cells to recognize and eliminate the invaders. This process enables the body to generate specific immunity, effectively protecting against future encounters with the same pathogen.
Furthermore, the lymphatic system plays a crucial role in the transportation of antigens – fragments of pathogens that trigger an immune response – to lymph nodes, facilitating the activation of antigen-presenting cells and the initiation of an adaptive immune response. This intricate process underscores the lymphatic system's pivotal function in coordinating immune surveillance and response throughout the body.
The Anatomy of Lymphatic System and Immune Defense
The intricate anatomy of the lymphatic system is integral to its role in defending against pathogens. Lymphatic vessels possess one-way valves that ensure the unidirectional flow of lymph, preventing backflow and maintaining a steady movement of the fluid. This structure not only aids in the removal of waste and cellular debris but also facilitates the transportation of immune cells to sites of infection or inflammation.
Moreover, the structure of lymph nodes – with a network of sinuses and compartments populated by immune cells – promotes the efficient detection and elimination of pathogens. The specialized architecture of these nodes enables the trapping and processing of antigens, allowing the immune system to mount an effective response to combat infection.
Conclusion
The lymphatic system's contribution to the body's defense against pathogens is a marvel of biological engineering. Its intricate network, comprising vessels, nodes, and organs, collaborates seamlessly to combat foreign invaders and maintain the body's immune vigilance. Understanding the anatomy and functions of the lymphatic system illuminates its significance in preserving health and underscores the crucial role it plays in the body's overall defense mechanism.