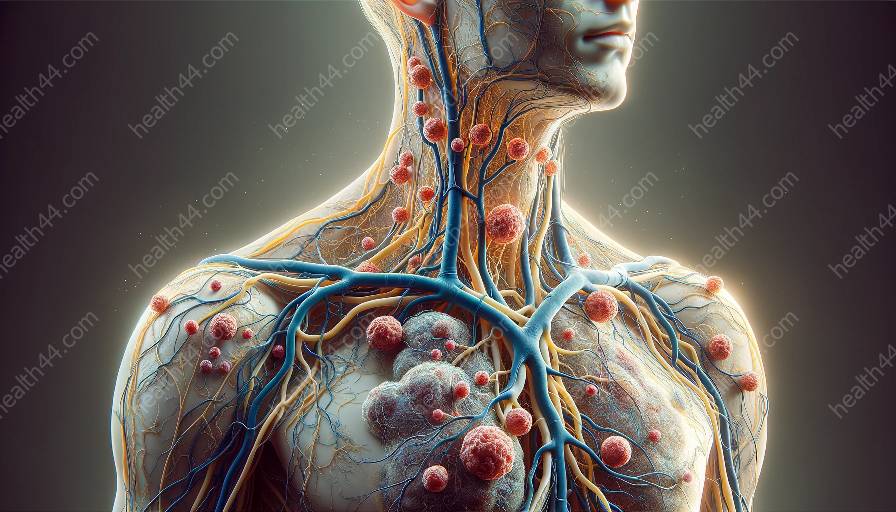
The lymphatic system is a vital part of the body's immune and circulatory systems, playing essential roles in maintaining fluid balance, fighting infections, and more. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the fascinating functions of the lymphatic system and its critical importance in anatomy.
Structure and Components of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is a network of tissues and organs that help rid the body of toxins, waste, and other unwanted materials. It includes lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, the spleen, thymus, and tonsils. Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures that act as filters along the lymphatic vessels. The lymphatic vessels carry lymph, a clear fluid that contains white blood cells, through the body.
Functions of the Lymphatic System
1. Immune Function
One of the primary functions of the lymphatic system is to support the body's immune response. Lymph nodes, which are found throughout the body, play a crucial role in filtering and trapping harmful substances, such as bacteria and viruses, and activating immune cells to destroy them. The lymphatic system also produces and stores white blood cells, including lymphocytes, which help fight off infections and diseases.
2. Fluid Balance
The lymphatic system plays a key role in maintaining fluid balance in the body. It helps to regulate the distribution of fluids by draining excess interstitial fluid from the body tissues and returning it to the bloodstream. This process helps prevent the buildup of excess fluid, known as edema, which can lead to swelling and discomfort.
3. Nutrient Absorption
In the small intestine, the lymphatic system plays a vital role in the absorption of dietary fats and fat-soluble vitamins. Specialized lymphatic vessels called lacteals absorb these nutrients from the digestive tract and transport them to the bloodstream for distribution throughout the body. This function is critical for maintaining overall health and proper nutrition.
4. Waste Removal
The lymphatic system is responsible for collecting and transporting waste products, cellular debris, and toxins away from the body tissues. Lymphatic vessels carry these waste materials to the lymph nodes, where they are filtered and ultimately eliminated from the body. This crucial function helps to keep the body clean and free from harmful substances.
5. Fluid and Immune Cell Transport
The lymphatic system serves as a transportation network for lymph, immune cells, and other essential substances. Lymphatic vessels carry lymph from the tissues to the bloodstream, helping to maintain fluid balance and deliver immune cells to areas of the body where they are needed most, such as sites of infection or inflammation.
Disorders and Diseases of the Lymphatic System
When the lymphatic system becomes compromised or impaired, it can lead to various disorders and diseases. Lymphedema, for example, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess lymphatic fluid, resulting in swelling, discomfort, and an increased risk of infections. Lymphoma, a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system, can also develop when abnormal lymphocytes multiply uncontrollably.
Conclusion
The lymphatic system is a complex and crucial network that supports the body's immunity, fluid balance, and overall health. Understanding its functions and significance in anatomy is essential for appreciating the body's intricate mechanisms of defense and maintenance. By exploring the functions of the lymphatic system, we gain valuable insight into the remarkable capabilities of the human body.