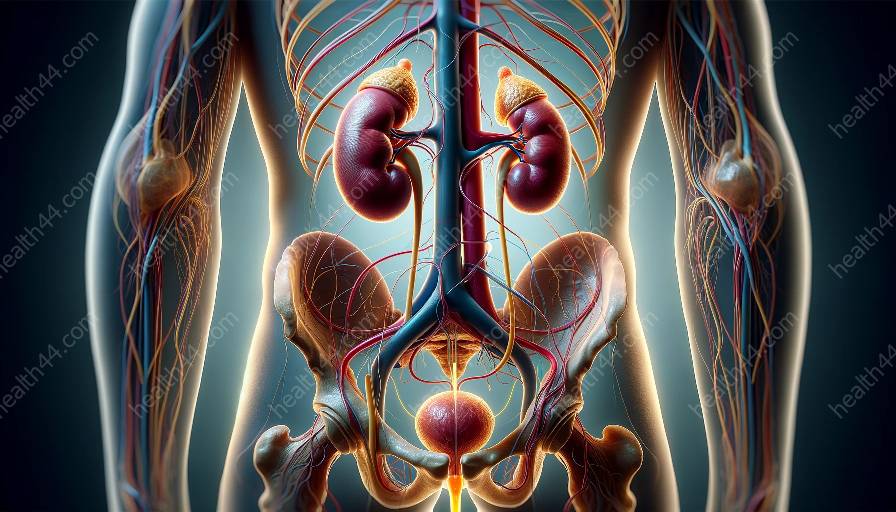
The urinary system is a vital component of the human body, responsible for several primary functions that ensure the body's overall health and stability. To understand the intricate workings of the urinary system and its structure, it is imperative to delve into urinary anatomy and explore its intricate details.
Anatomy of the Urinary System:
The urinary system is comprised of several key structures, each playing a crucial role in maintaining the body's fluid and electrolyte balance, eliminating waste products, and regulating blood pressure. The primary anatomical components of the urinary system include the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
Kidneys:
The kidneys, positioned in the upper abdominal cavity, are bean-shaped organs responsible for filtering blood and producing urine. They maintain the body's overall fluid balance, regulate electrolyte levels, and eliminate waste products from the bloodstream through urine formation.
Ureters:
The ureters are slender tubes that connect the kidneys to the urinary bladder, facilitating the transport of urine from the kidneys to the bladder. These muscular tubes utilize peristaltic contractions to propel urine toward the bladder, maintaining the unidirectional flow of urine.
Urinary Bladder:
The urinary bladder serves as a reservoir for urine storage before its eventual elimination from the body. This muscular organ expands and contracts to accommodate varying volumes of urine, with the assistance of the internal urethral sphincter that regulates the flow of urine from the bladder.
Urethra:
The urethra is a tube that extends from the urinary bladder to the exterior of the body, enabling the expulsion of urine during urination. In males, the urethra also serves a dual purpose by transporting semen during ejaculation.
Primary Functions of the Urinary System:
The primary functions of the urinary system are essential for maintaining homeostasis and eliminating waste products from the body. These functions are intricate and highly coordinated, contributing to the overall well-being of an individual.
Filtration and Excretion:
One of the central functions of the urinary system is the filtration of blood to remove waste products and excess substances. The kidneys play a pivotal role in this process by filtering the blood and producing urine, which contains waste products such as urea, creatinine, and excess ions. Effective excretion of these waste products is vital for preventing their accumulation in the body, which can lead to toxicity and impaired organ function.
Regulation of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance:
The urinary system regulates the body's fluid and electrolyte balance by adjusting the volume and composition of urine based on varying internal and external conditions. This function is crucial for maintaining proper hydration, blood pressure, and overall physiological stability.
Acid-Base Balance:
Acid-base balance is essential for maintaining the body's pH within a narrow range to support various physiological processes. The urinary system helps regulate acid-base balance by selectively reabsorbing or excreting hydrogen ions and bicarbonate ions in response to changes in blood pH.
Blood Pressure Regulation:
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, which is intricately linked to the urinary system, plays a pivotal role in regulating blood pressure. The kidneys release renin in response to decreased blood pressure or decreased sodium levels, initiating a cascade of events that ultimately lead to vasoconstriction and the retention of water and sodium to help raise blood pressure.
Production of Hormones:
Beyond its excretory functions, the kidneys also produce and release several important hormones. These include erythropoietin, which stimulates red blood cell production, and calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D, which regulates calcium and phosphorus metabolism.
The Role of Urinary System in Overall Health:
The proper functioning of the urinary system is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Any disruption in the urinary system's functions can lead to various health issues, including electrolyte imbalances, fluid retention, and the accumulation of waste products in the body. Understanding the anatomy and functions of the urinary system is crucial for appreciating its importance in maintaining the body's internal equilibrium.
In conclusion, the urinary system is an intricate and indispensable component of the human body, contributing to vital physiological functions and playing a pivotal role in maintaining overall health. Exploring urinary anatomy alongside the primary functions of the urinary system provides a comprehensive understanding of its significance, highlighting the interdependence of anatomical structures and physiological processes.