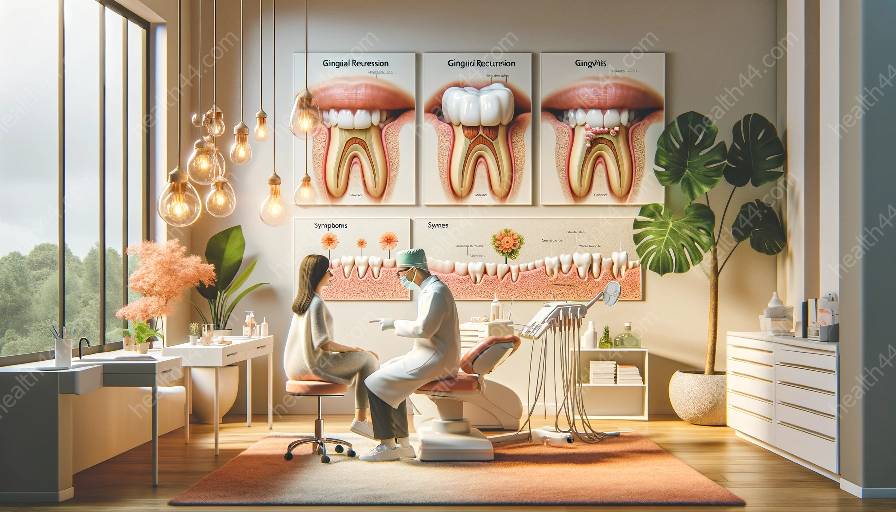
Proper oral hygiene plays a crucial role in the development and prevention of gingival recession and gingivitis. To fully understand how oral hygiene affects these conditions, it's essential to delve into the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options.
The Connection Between Oral Hygiene and Gingival Recession
Gingival recession, also known as receding gums, is the exposure of the roots of the teeth due to a loss of gum tissue and attachment. Poor oral hygiene is a significant contributor to the development of gingival recession. When plaque and tartar accumulate along the gumline, they can lead to inflammation and bacterial infection, causing the gums to recede over time. Inadequate brushing and flossing habits can exacerbate this process, ultimately resulting in gingival recession.
Impact of Oral Hygiene Practices
Oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, are essential for maintaining healthy gums and preventing gingival recession. Proper brushing helps remove plaque and bacteria from the teeth and gumline, reducing the risk of gum disease and recession. Flossing is equally important, as it removes food particles and plaque from between the teeth and along the gumline, preventing the accumulation of harmful bacteria.
The Role of Diet in Oral Hygiene
In addition to brushing and flossing, a balanced diet also plays a crucial role in maintaining good oral hygiene. Foods high in sugar and carbohydrates can contribute to the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth, leading to gum disease and gingival recession. On the other hand, consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and calcium can help strengthen the teeth and gums.
Relation Between Oral Hygiene and Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the inflammation of the gums caused by the accumulation of plaque and tartar. Poor oral hygiene is the primary factor contributing to the development of gingivitis. When plaque is not effectively removed through proper brushing and flossing, it can irritate the gums, leading to inflammation and tenderness. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to more severe forms of gum disease, including periodontitis and gingival recession.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing gingival recession and gingivitis requires a multi-faceted approach that includes proper oral hygiene practices, regular dental check-ups, and a healthy lifestyle. Brushing at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and scheduling regular dental cleanings are essential for preventing and managing these conditions. Additionally, avoiding tobacco products and maintaining a balanced diet can contribute to overall oral health.
Professional Intervention
If gingival recession or gingivitis is already present, seeking professional dental care is crucial. Dentists can provide deep cleanings, scaling, and root planing to remove plaque and tartar from below the gumline, helping to restore gum health. In more advanced cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to repair the damaged gum tissue and prevent further recession.
Conclusion
In conclusion, oral hygiene has a direct impact on the development and progression of gingival recession and gingivitis. By practicing good oral hygiene, including brushing, flossing, and maintaining a healthy diet, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing these conditions. Understanding the connection between oral hygiene and gum health is essential for maintaining a healthy smile and overall well-being.