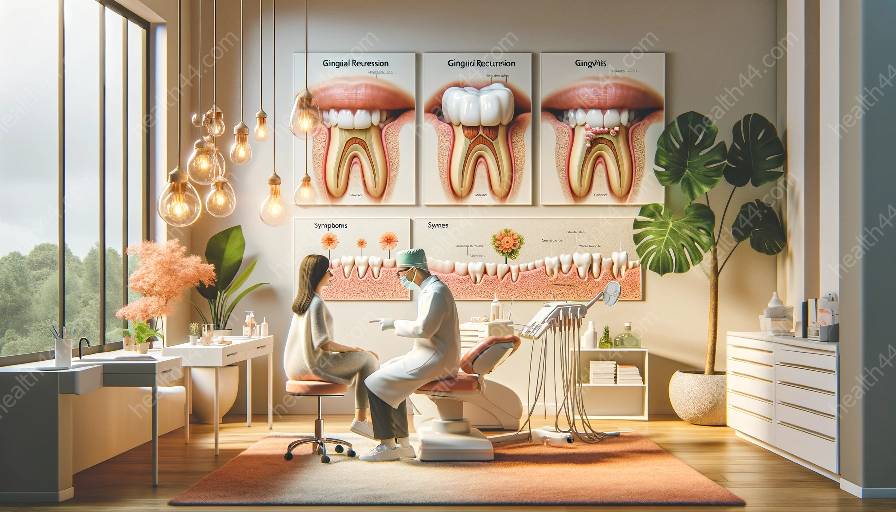
Gingival recession is a condition where the gum tissue pulls back, exposing the roots of the teeth. While there are various surgical procedures available to treat gingival recession, they come with certain risks that patients should be aware of. It's important to understand these risks and their potential impact on gingivitis, another common periodontal condition.
Understanding Gingival Recession and Gingivitis
Gingival recession occurs when the margin of the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away or pulls back, leading to exposure of the tooth's root. This can result in a range of dental issues, including tooth sensitivity, decay, and an unattractive appearance. Furthermore, gingival recession can also increase the risk of developing gingivitis, an inflammatory condition of the gums caused by plaque buildup.
Risks Associated with Surgical Procedures
While surgical procedures are often recommended to address gingival recession, they carry certain risks that patients should consider. These risks include:
- Postoperative Pain and Discomfort: Following surgical treatment, patients may experience pain and discomfort, which can persist for several days or weeks.
- Swelling and Bruising: Swelling and bruising are common side effects of surgical procedures, especially in the treated area. This can affect the patient's appearance and may take some time to resolve.
- Complications with Healing: In some cases, the surgical site may experience delayed or impaired healing, leading to potential infections or other complications.
- Tooth Sensitivity: Surgical procedures may result in increased tooth sensitivity, particularly to hot, cold, or sweet stimuli, which can be uncomfortable for the patient.
- Recession Persistence: Despite undergoing surgical treatment, there is a possibility of recession persistence, especially if the underlying cause of the recession is not adequately addressed.
- Root Surface Exposure: Surgical techniques may inadvertently expose the roots of the teeth, leading to further complications and increased susceptibility to decay.
Impact on Gingivitis
Understanding the risks associated with surgical procedures for treating gingival recession is crucial, particularly in relation to their impact on gingivitis. Since gingival recession can contribute to an increased risk of gingivitis, it is important to consider how surgical interventions may influence this condition.
Given the potential postoperative pain, swelling, and delayed healing associated with surgical procedures, patients undergoing treatment for gingival recession may experience challenges in maintaining proper oral hygiene, which is crucial for preventing and managing gingivitis. Additionally, the exposure of the tooth's root as a result of recession and subsequent surgical treatment may contribute to an increased susceptibility to plaque accumulation, further exacerbating the risk of developing or worsening gingivitis.
Minimizing Risks and Optimizing Outcomes
While surgical procedures for treating gingival recession pose certain risks, there are measures that can be taken to minimize these risks and optimize the outcomes. These include:
- Preoperative Evaluation: Thorough evaluation of the patient's oral health and risk factors can help identify potential challenges and optimize treatment planning.
- Expertise and Precision: Seeking treatment from experienced periodontal specialists who employ precise surgical techniques can reduce the risk of complications and improve outcomes.
- Postoperative Care: Following proper postoperative care instructions, including oral hygiene practices and medication adherence, can support successful healing and reduce the likelihood of complications.
- Regular Monitoring and Maintenance: Routine follow-up visits with the dental care team can allow for ongoing monitoring of the surgical site and proactive intervention if any issues arise.
- Addressing Underlying Factors: Identifying and addressing the underlying causes of gingival recession, such as malocclusion or aggressive tooth brushing, can help prevent recurrence and improve long-term outcomes.
By being informed about the risks associated with surgical procedures for treating gingival recession, and understanding their potential impact on gingivitis, patients can make educated decisions about their oral health care. Working closely with their dental care team and following recommended guidelines can help mitigate risks and achieve favorable outcomes.