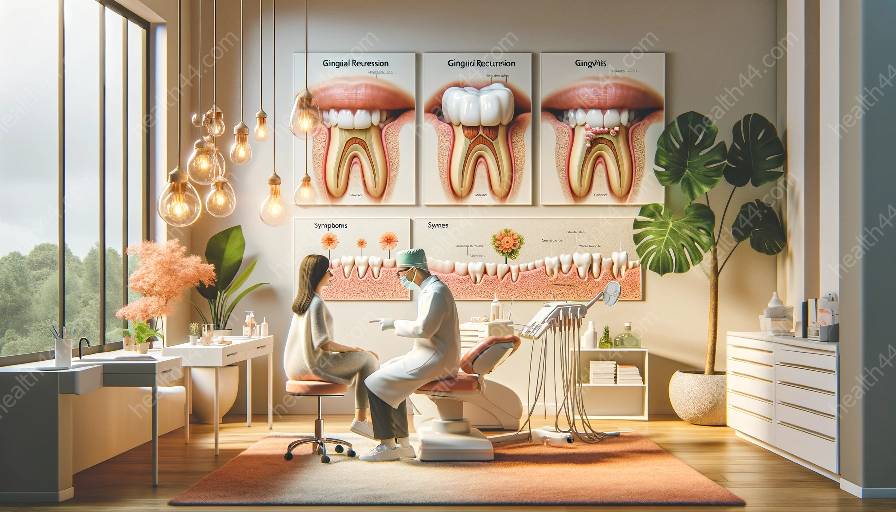
Gingival recession is a common dental condition that involves the gradual withdrawal of the gum tissue, leading to exposure of the tooth root. This problem becomes more prevalent in the elderly population, posing a variety of challenges for oral health professionals and patients alike. Understanding the causes, consequences, and treatment options for gingival recession in the elderly can help mitigate its impact and improve quality of life for affected individuals.
Causes of Gingival Recession in the Elderly
Several factors contribute to the development of gingival recession in the elderly population. One major cause is periodontal disease, which encompasses gingivitis and its more advanced form, periodontitis. These conditions lead to inflammation and damage to the gum tissue, causing it to recede over time. Other potential causes include aggressive tooth brushing, anatomical factors such as thin gum tissues, and inadequate dental care over the years.
Consequences of Gingival Recession
Gingival recession can have various consequences for the elderly population. Exposed tooth roots are more susceptible to decay and sensitivity, leading to discomfort and difficulty in maintaining oral hygiene. Furthermore, the aesthetic impact of gingival recession can affect an individual's self-esteem, especially in a society that often associates a youthful appearance with healthy gums.
Connection Between Gingival Recession and Gingivitis
Gingivitis is an early stage of periodontal disease and is characterized by inflammation of the gums. While not solely responsible for the development of gingival recession, untreated gingivitis can lead to more severe periodontal disease, which in turn increases the likelihood of gingival recession. As such, managing and preventing gingivitis is essential in reducing the risk of gingival recession in the elderly.
Treatment Options for Gingival Recession
Managing gingival recession in the elderly population involves a multi-faceted approach. This may include professional dental cleanings to remove plaque and tartar, as well as addressing any underlying periodontal disease. Surgical interventions such as gum grafting or the use of regenerative materials can also help to restore gum tissue and cover exposed tooth roots. In addition, modifying oral hygiene practices, such as using a softer toothbrush and adopting gentle brushing techniques, can contribute to preventing further recession.
Conclusion
Gingival recession in the elderly population is a complex issue that demands attention and proactive management. By understanding its causes, consequences, and treatment options, both oral health professionals and patients can work together to mitigate the impact of this condition and improve the oral health and well-being of the elderly population.