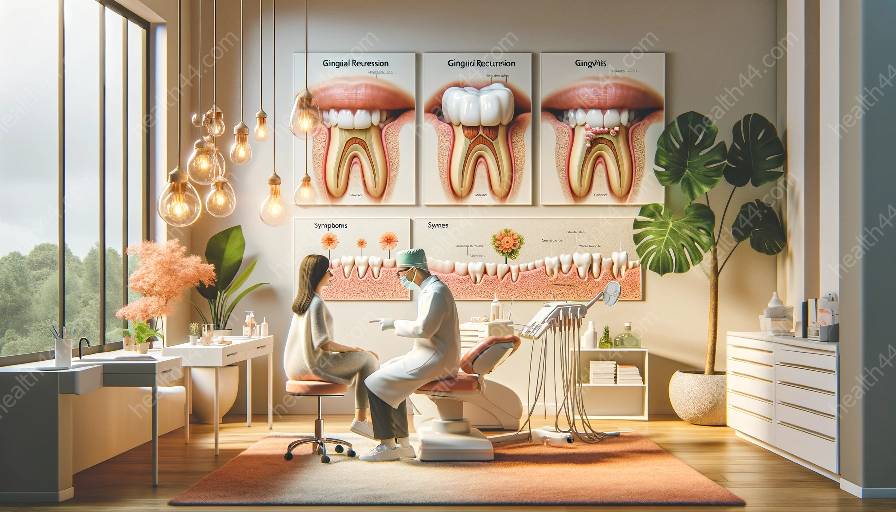
Gingival recession is a common oral health issue that can have psychosocial implications. In this article, we will delve into the psychosocial impact of gingival recession, its connection with gingivitis, and its overall effects on individuals' emotional and social well-being.
Gingival Recession and Its Psychological Impact
Gingival recession occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth pulls back and exposes the tooth root. This condition can lead to a range of emotional and psychological challenges for individuals. One of the primary impacts of gingival recession is related to self-esteem and confidence. The visible appearance of receding gums can significantly affect a person's self-image and confidence levels. Individuals may feel self-conscious about their smile, leading to a decline in their social interactions and overall quality of life.
In addition, individuals with gingival recession may experience anxiety and worry about their oral health. The fear of tooth sensitivity, oral discomfort, and potential long-term consequences can lead to increased stress and psychological distress.
The psychosocial impact of gingival recession can also extend beyond individual well-being to affect interpersonal relationships. Some individuals may feel embarrassed or insecure about their smile, which can impact their ability to engage in social activities and maintain healthy relationships.
The Link Between Gingival Recession and Gingivitis
Gingival recession is often associated with gingivitis, an inflammatory condition of the gums. The development of gingivitis can exacerbate the psychosocial impact of gingival recession. The discomfort, pain, and aesthetic changes associated with gingivitis can further contribute to emotional distress and social withdrawal. This interconnectedness underscores the importance of addressing both gingival recession and gingivitis in a comprehensive manner.
Moreover, the chronic nature of gingival recession and gingivitis can lead to long-term psychological effects if left unmanaged. Individuals may struggle with ongoing anxiety, self-esteem issues, and social isolation, highlighting the necessity of timely intervention and support.
The Holistic Approach to Oral Health
Understanding the psychosocial impact of gingival recession emphasizes the need for a holistic approach to oral health care. It is essential for dental professionals to not only address the physical aspects of gingival recession and gingivitis but also consider the emotional and psychological well-being of their patients.
This holistic approach entails open communication, empathy, and tailored support to address the psychosocial concerns related to gingival recession. Dental professionals can offer education, counseling, and treatment options to help individuals manage their emotional responses, improve their self-image, and regain their confidence in social settings.
Furthermore, promoting awareness and understanding of the psychosocial impact of gingival recession within the wider community can foster empathy and support for individuals dealing with this condition. By acknowledging the emotional challenges associated with gingival recession, society can contribute to creating a more inclusive and compassionate environment for those affected.
Conclusion
Gingival recession can have far-reaching psychosocial effects that extend beyond the physical symptoms. The emotional and social impact of this condition underscores the importance of addressing both physical and psychological aspects of oral health. By recognizing the interconnectedness of gingival recession with gingivitis and the emotional well-being of individuals, holistic oral health care can be promoted, enhancing overall quality of life.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the psychosocial impact of gingival recession is crucial for promoting empathy, providing effective support, and enhancing the well-being of individuals affected by this condition.