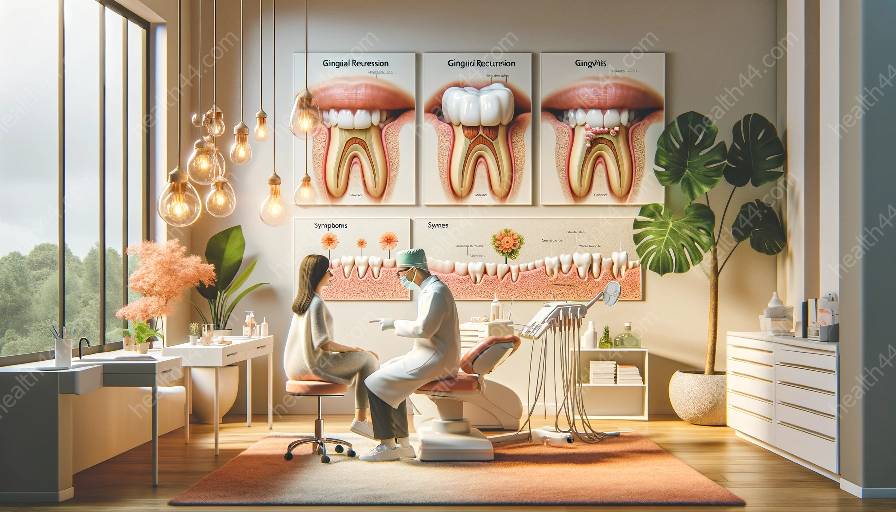
Gingival recession, which refers to the loss of gum tissue, is a common dental condition that can result from various factors, including medications and gingivitis. Understanding the connection between medications and gingival recession is essential for effective oral health management.
Gingival Recession: A Brief Overview
Gingival recession occurs when the gums pull back from the tooth, exposing the root surfaces. This can lead to tooth sensitivity, aesthetic concerns, and other dental problems. While gingival recession can be caused by several factors, including aggressive tooth brushing and periodontal diseases, the potential impact of medications on gum health is often overlooked.
Medications and Gingival Recession
Various medications have been associated with gingival recession. Some medications, specifically antiseizure drugs and immunosuppressants, may lead to gum tissue overgrowth, which can contribute to gingival recession. In contrast, certain medications, such as some calcium channel blockers and immunosuppressants, have been linked to gingival overgrowth, which can increase the risk of gingivitis and periodontal disease. These drug-induced changes in gum tissue can significantly impact oral health.
Medications and Gingivitis
Gingivitis, an inflammation of the gums, can be exacerbated by certain medications as well. Medications that decrease saliva flow, such as antihistamines, decongestants, and some antidepressants, can contribute to dry mouth, which increases the risk of gingivitis. Additionally, some medications may cause changes in the composition of saliva, promoting the growth of bacteria and leading to gum inflammation.
Strategies for Managing Oral Health in Connection with Medications
Given the potential impact of medications on gingival recession and gingivitis, it is crucial to adopt effective strategies for managing oral health in connection with these medications. Here are some important steps to consider:
- Open Communication with Healthcare Providers: Discuss any concerns about medication-related effects on oral health with your healthcare providers to explore potential alternatives or preventive measures.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Schedule regular dental check-ups to monitor the condition of your gums and address any signs of gingival recession or gingivitis at an early stage.
- Optimal Oral Hygiene: Maintain proper oral hygiene practices, including gentle brushing, flossing, and the use of antimicrobial mouthwash, to minimize the risk of gum disease.
- Saliva Stimulation: If medications are causing dry mouth, consider using saliva-stimulating products or sugar-free gum to help alleviate dryness and reduce the risk of gingivitis.
- Evaluating Medication Options: Work with your healthcare providers to evaluate the potential impact of medications on oral health and explore alternative options if necessary.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between medications and gingival recession, as well as their impact on gingivitis, is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health. By being proactive and informed, individuals can take steps to mitigate the potential adverse effects of medications on their gums and overall oral health.