With a focus on gingival recession, this topic cluster will explore the interplay between gingival recession, gingivitis, and restorative treatments. We will delve into the causes, effects, and potential treatment options, providing a comprehensive understanding of the complex relationship and offering insights into promoting gingival health.
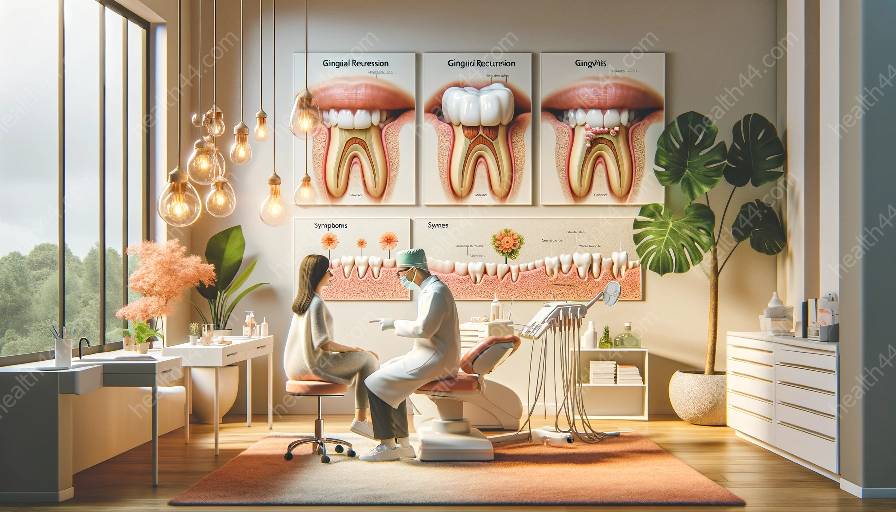
Gingival Recession: Causes and Effects
Gingival recession is a condition characterized by the progressive loss of gum tissue, leading to the exposure of the roots of the teeth. It can result from various factors, including aggressive tooth brushing, periodontal disease, genetic predisposition, or anatomical factors.
The consequences of gingival recession can extend beyond cosmetic concerns, impacting dental health. Exposed tooth roots are more susceptible to decay and may cause tooth sensitivity. Additionally, compromised gum tissue can lead to an increased risk of further recession and tooth mobility.
Gingivitis and Its Role in Gingival Recession
Gingivitis, characterized by inflammation and bleeding of the gums, plays a crucial role in the development of gingival recession. Poor oral hygiene, plaque accumulation, and bacterial infections can contribute to gingivitis, which, if left untreated, may progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that can accelerate gingival recession.
Understanding the link between gingivitis and gingival recession is essential for effective prevention and management. Addressing gingivitis and maintaining gum health can mitigate the risk of progressive recession and associated complications.
Restorative Treatments for Gingival Recession
Successful management of gingival recession often involves a combination of preventive measures and restorative treatments. Non-surgical approaches may include scaling and root planing to address underlying periodontal conditions and promote gum tissue regeneration. Additionally, orthodontic interventions, such as braces or aligners, can help redistribute forces on the teeth and reduce recession.
In cases where recession is more advanced, surgical techniques like gum grafting or guided tissue regeneration may be necessary to restore gum volume and cover exposed roots. These restorative procedures aim to improve both the esthetic and functional aspects of the affected area, providing long-term stability and protection for the teeth.
Promoting Successful Restorative Treatments
For restorative treatments to yield optimal results, a comprehensive approach that targets both the underlying causes of gingival recession and related gingival health is crucial. Implementing effective oral hygiene practices, seeking timely professional dental care, and addressing predisposing factors, such as malocclusion and aggressive brushing, can contribute to the success of restorative interventions.
Furthermore, patient education and regular follow-ups play a significant role in ensuring the longevity of restorative outcomes. Encouraging a partnership between dental professionals and patients fosters a supportive environment for ongoing maintenance and preventive measures, ultimately enhancing the success of restorative treatments.