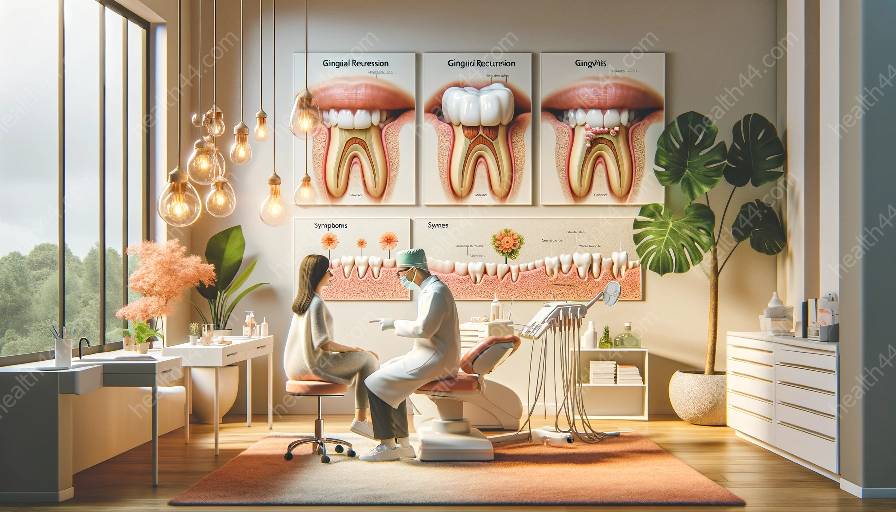
Gingival recession is a common condition where the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away or pulls back, exposing the tooth roots. This can lead to several potential long-term complications, especially if left untreated. Gingival recession is closely related to gingivitis, an early stage of gum disease, and understanding their connection is essential for maintaining oral health.
1. Increased Tooth Sensitivity
As the root of the tooth becomes exposed due to gingival recession, individuals may experience increased sensitivity to hot, cold, and sweet foods and beverages. This heightened sensitivity can make consuming certain foods and drinks uncomfortable or even painful.
2. Tooth Decay and Cavities
Exposure of the tooth roots makes them more susceptible to decay and cavities. Unlike the hard enamel covering the crown of the tooth, the roots are covered by cementum, a softer tissue that is more prone to decay. Without the protection of gum tissue, the roots become vulnerable to bacterial attack and subsequent tooth decay.
3. Periodontal Disease Progression
Gingival recession is often associated with the progression of periodontal disease, a more serious form of gum disease. When gum recession occurs, it can lead to deeper gum pockets, which are difficult to clean and become a breeding ground for bacteria. This can result in an increased risk of infection and inflammation, leading to periodontal disease.
4. Esthetic Concerns
Gingival recession can cause an unsightly appearance, as it exposes the roots of the teeth and creates a notched or elongated look. This can lead to self-consciousness and dissatisfaction with one's smile, affecting individuals' confidence and quality of life.
5. Gum Erosion and Bone Loss
Chronic gingival recession can lead to erosion of the gum tissue and underlying bone, which supports the teeth. This can result in a weakening of the tooth's foundation, potentially leading to tooth loss in severe cases.
6. Compromised Tooth Stability
As the supporting gum and bone structures erode due to gingival recession, the stability of the affected teeth may be compromised. This can ultimately lead to tooth mobility and the need for dental interventions, such as implants or other restorative procedures.
7. Impact on Overall Health
Research has indicated potential links between oral health, including gingival recession, and systemic conditions such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes. While the direct causative relationship is still being studied, maintaining healthy gums and addressing gingival recession may have broader implications for overall health.
It is important to note that gingival recession and its long-term complications are closely interlinked with gingivitis. Gingivitis, characterized by inflammation of the gums, is often the precursor to gingival recession and its associated issues. Addressing gingivitis through proper oral hygiene and professional dental care can help prevent the development and progression of gingival recession and its potential complications.
Understanding and addressing the potential long-term complications of gingival recession is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health and overall well-being. By recognizing the risks and taking proactive steps, individuals can work towards preventing and managing gingival recession and its associated issues.