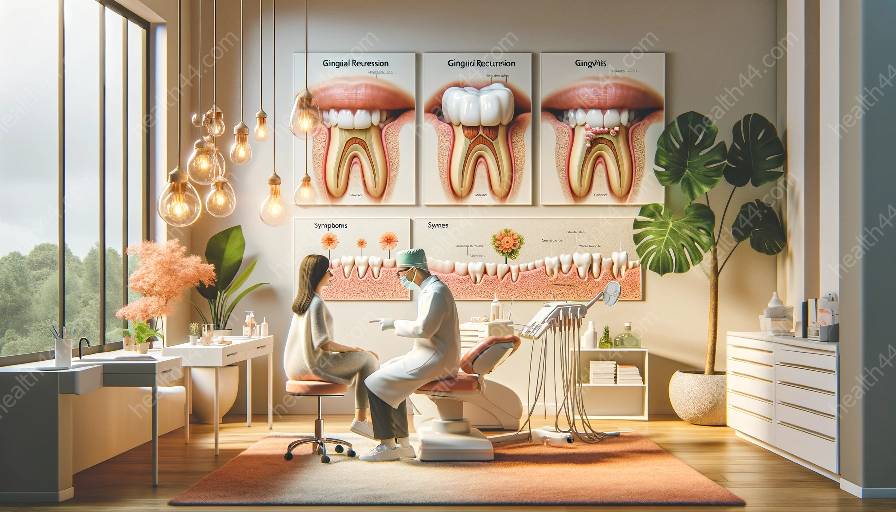
Gingival recession, a common oral health problem, occurs when the gums recede or pull back from the teeth, exposing the roots. Understanding the relationship between medications and gingival recession is crucial in maintaining good oral health. Medications can play a significant role in contributing to the development of gingival recession, especially when coupled with the presence of gingivitis.
Medications and Gingival Recession
Various medications have been associated with gingival recession, including but not limited to:
- Anti-Seizure Medications: Certain anti-seizure medications can cause gingival overgrowth, which in turn may contribute to gingival recession by creating an environment in which the gums are more susceptible to recession.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: These drugs are used to treat high blood pressure and heart conditions. In some cases, they may lead to gingival overgrowth, potentially exacerbating the risk of gingival recession.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications used to suppress the immune system, such as those administered after organ transplants, have been linked to gingival overgrowth, which can be a precursor to gingival recession.
Impact of Gingivitis
Gingivitis, the inflammation of the gums, can also be a contributing factor to the development of gingival recession. When the gums are inflamed due to the presence of plaque and bacteria, they become more sensitive and susceptible to recession. Additionally, medications that cause gingival overgrowth can exacerbate the effects of gingivitis, leading to an increased risk of gingival recession.
Preventive Measures
Understanding the role of medications in the development of gingival recession emphasizes the need for preventive measures and proactive oral care. It is imperative for individuals taking medications associated with gingival overgrowth to practice meticulous oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups to monitor their gum health. Moreover, maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle can support overall oral health and reduce the risk of gingival recession.
Treatment and Management
For individuals already experiencing gingival recession, seeking professional dental care is essential. Treatment options may include gum grafting, which involves taking tissue from the roof of the mouth and attaching it to the affected area to cover the exposed roots. Additionally, oral health professionals may recommend specific oral care routines to alleviate the progression of gingival recession and mitigate its impact.
Conclusion
The interplay between medications, gingival recession, and gingivitis underscores the importance of holistic oral care. Awareness of the potential impact of certain medications on gum health can aid in preventing and managing gingival recession. By actively addressing the factors contributing to the development of gingival recession, individuals can prioritize their oral health and minimize the potential risks associated with medications.