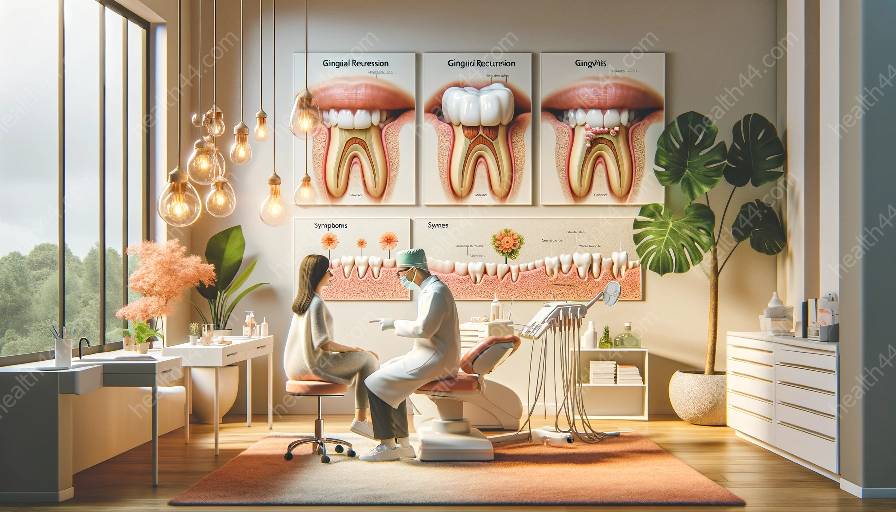
Gingival recession and untreated gingivitis can lead to various long-term complications that significantly impact oral health and overall well-being. Let's explore the potential consequences of leaving gingival recession untreated, its interrelation with gingivitis, and measures for prevention and intervention.
The Basics of Gingival Recession and Gingivitis
Gingival recession refers to the exposure of the roots of the teeth due to the loss of gum tissue. This condition can result from multiple factors, including aggressive tooth brushing, periodontal disease, and genetics. Conversely, gingivitis, an early form of gum disease, is characterized by inflamed and bleeding gums caused by bacterial plaque buildup.
When left untreated, both gingival recession and gingivitis can progress and lead to severe long-term complications. It is essential to understand the potential impact of these conditions to prevent further oral health deterioration.
Interrelation Between Gingival Recession and Gingivitis
The presence of gingival recession and gingivitis often coincides and exacerbates their individual effects. The exposed tooth roots due to gingival recession are more prone to plaque accumulation, causing an increased risk of gum inflammation and leading to the progression of gingivitis. In turn, untreated gingivitis can contribute to further gum recession, creating a vicious cycle that exacerbates oral health issues.
Understanding this interrelation is crucial in addressing the long-term complications associated with untreated gingival recession and its relationship with gingivitis.
Potential Long-Term Complications of Untreated Gingival Recession
1. Tooth Decay and Sensitivity
The exposure of tooth roots caused by gingival recession can lead to increased susceptibility to tooth decay and sensitivity. Without the protective covering of gum tissue, the roots become more prone to decay and discomfort, requiring prompt intervention to prevent further complications.
2. Gum Inflammation and Periodontal Disease
Untreated gingival recession can contribute to the development of periodontal disease, a severe gum infection that can damage the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth. As the condition progresses, tooth loss becomes a significant risk, emphasizing the need for proactive measures to address the underlying issues.
3. Compromised Aesthetic Appeal
Gingival recession can also lead to aesthetic concerns, such as uneven gum lines and tooth exposure, impacting an individual's smile and confidence. These aesthetic implications highlight the multifaceted impact of untreated gingival recession beyond physical discomfort and oral health challenges.
Preventive and Interventional Measures
Addressing the long-term complications of untreated gingival recession and its relationship with gingivitis requires a comprehensive approach involving preventive measures and timely interventions.
Prevention
Proper oral hygiene practices, including gentle brushing, daily flossing, and regular dental check-ups, play a crucial role in preventing the progression of gingival recession and gingivitis. Additionally, avoiding tobacco use and maintaining a balanced diet can significantly contribute to overall oral health.
Interventions
Seeking professional dental care is essential in managing and treating gingival recession and gingivitis. Dentists may recommend interventions such as gum grafting, scaling and root planing, or other periodontal treatments to address the underlying issues and prevent further complications.
Conclusion
Gingival recession, when left untreated, can result in significant long-term complications that impact oral health, overall well-being, and aesthetic considerations. Understanding its interrelation with gingivitis is vital in addressing these complications and implementing preventive and interventional measures to maintain optimal oral health. By recognizing the potential consequences and taking proactive steps, individuals can effectively manage and mitigate the impact of untreated gingival recession, promoting long-term oral health and wellness.