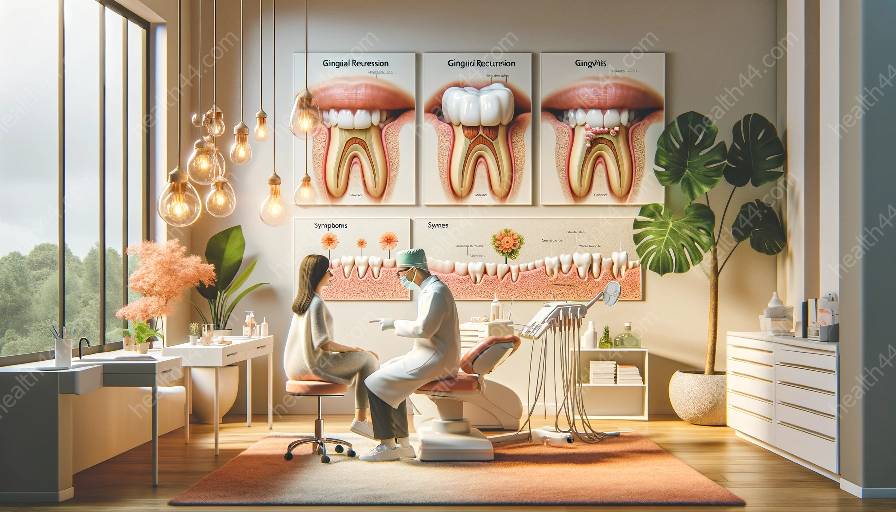
Gingival recession, commonly associated with gingivitis, can be managed with various surgical techniques that aim to restore gum health. This article explains the treatment options and procedures available for addressing gingival recession and its relationship with gingivitis.
Gingival Recession: Causes and Relationship with Gingivitis
Gingival recession refers to the exposure of the roots of the teeth due to the loss of gum tissue. It can be caused by multiple factors, including aggressive tooth brushing, periodontal diseases, anatomical factors, and trauma. When left untreated, gingival recession can lead to increased sensitivity, aesthetic concerns, and potential root caries.
Gingivitis, on the other hand, is an inflammation of the gums caused by plaque buildup and poor oral hygiene. If not managed effectively, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which can further contribute to gingival recession.
Understanding the relationship between gingival recession and gingivitis is crucial in designing comprehensive treatment plans that address both conditions.
Non-Surgical Approaches for Managing Gingival Recession
Before considering surgical interventions, non-surgical approaches are often recommended to manage gingival recession. These may include:
- Professional Scaling and Root Planing: This deep cleaning procedure removes plaque and calculus from the tooth surfaces and below the gumline, promoting healing and reducing inflammation.
- Improving Oral Hygiene: Educating patients about proper brushing and flossing techniques and the use of antimicrobial mouth rinses can help manage gingivitis and prevent further recession.
- Modification of Risk Factors: Identifying and addressing risk factors such as aggressive tooth brushing, malocclusion, and tobacco use can play a critical role in preventing progression of gingival recession.
While these non-surgical approaches are important in the management of gingival recession and gingivitis, some cases may require surgical intervention to achieve optimal results.
Surgical Techniques for Managing Gingival Recession
When non-surgical methods are insufficient to address gingival recession, surgical techniques may be indicated. There are several surgical procedures commonly used to manage gingival recession, including:
1. Root Coverage Procedures:
Root coverage procedures, such as the coronally positioned flap and the laterally positioned flap, involve shifting and repositioning existing gum tissue to cover the exposed root surfaces. These techniques aim to enhance the aesthetics of the smile and reduce root sensitivity.
2. Connective Tissue Grafting:
Connective tissue grafting involves harvesting tissue from the patient's palate and transplanting it to the affected areas to augment the gum tissue. This procedure helps restore adequate gingival thickness and address aesthetic concerns.
3. AlloDerm Grafting:
AlloDerm grafting utilizes processed donor tissue to augment the gum tissue, eliminating the need for tissue harvesting from the patient's own palate. This can reduce post-operative discomfort and facilitate faster healing.
4. Tunneling Techniques:
Tunneling techniques involve the creation of a tunnel within the gum tissue to allow for the repositioning of the tissue and coverage of the exposed roots. This approach can minimize post-operative discomfort and enhance the esthetic outcomes.
Assessment and Planning for Surgical Interventions
Prior to performing any surgical procedure for managing gingival recession, a thorough assessment and meticulous planning are essential. This includes:
- Evaluation of Gingival Biotype: Understanding the thickness and characteristics of the patient's gum tissue is crucial in determining the most suitable surgical approach.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying and addressing potential risk factors, such as smoking, uncontrolled diabetes, and compromised oral hygiene, can influence the success and outcomes of the surgical interventions.
- Collaborative Approach: Involving periodontists, prosthodontists, and restorative dentists in the planning process ensures comprehensive care and coordinated treatment outcomes.
By comprehensively assessing and planning for surgical interventions, dental professionals can optimize the success of the procedures and enhance patient satisfaction.
Post-Operative Care and Follow-Up
Following surgical interventions for gingival recession, appropriate post-operative care and regular follow-up appointments are vital for ensuring successful outcomes. Patients should receive detailed instructions for post-operative management, including:
- Oral Hygiene Guidelines: Proper oral hygiene practices are essential for promoting healing and preventing complications following surgical procedures.
- Medication Management: Prescribing analgesics, antimicrobials, and anti-inflammatory medications as needed can help manage post-operative discomfort and reduce the risk of infection.
- Management of Complications: Patients should be educated about potential complications, such as swelling, bleeding, and graft failure, and instructed on when to seek immediate dental care.
Additionally, regular follow-up appointments allow the dental team to monitor healing, evaluate the success of the procedures, and address any concerns or complications that may arise.
Conclusion
Effective management of gingival recession involves a comprehensive understanding of the condition, its relationship with gingivitis, and the various treatment options available. Surgical techniques play a valuable role in restoring gum health, improving aesthetics, and reducing sensitivity associated with gingival recession. By employing evidence-based approaches and personalized treatment plans, dental professionals can achieve successful outcomes and enhance the overall oral health and well-being of their patients.