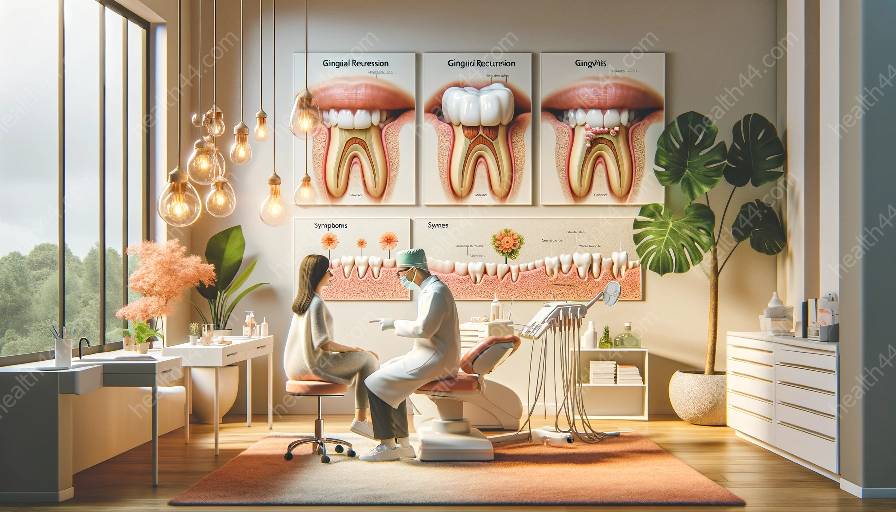
The connection between gingival recession and tooth mobility is a crucial aspect of oral health that requires attention and understanding. In this guide, we will explore the relationship between these two conditions, their impact on overall oral health, and their association with gingivitis.
Gingival Recession: An Overview
Gingival recession, also known as receding gums, occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth pulls back, exposing the tooth roots. This condition can lead to increased tooth sensitivity and a higher risk of dental issues such as decay and tooth loss. Several factors can contribute to gingival recession, including poor oral hygiene, aggressive tooth brushing, genetic predisposition, and gum disease.
Tooth Mobility: Understanding the Issue
Tooth mobility refers to the movement or looseness of the teeth within the jawbone. It is often a result of bone loss and weakening of the periodontal ligament that supports the teeth. While mild tooth mobility may not be noticeable, severe mobility can significantly impact a person's ability to chew and speak properly. Common causes of tooth mobility include periodontal disease, trauma, and habits such as tooth grinding.
The Relationship Between Gingival Recession and Tooth Mobility
The link between gingival recession and tooth mobility lies in their shared association with gum disease, specifically gingivitis. Gingivitis is an early stage of gum disease characterized by inflammation of the gum tissue caused by the accumulation of plaque and bacteria. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which affects the supporting structures of the teeth, leading to gum recession and tooth mobility.
Impact on Oral Health
Both gingival recession and tooth mobility pose significant threats to oral health. When the gums recede, the roots of the teeth become exposed, making them more vulnerable to decay and sensitivity. Additionally, the loss of gum tissue compromises the support structure of the teeth, contributing to increased tooth mobility. As a result, individuals with gingival recession are at a higher risk of experiencing tooth loss and other dental complications.
Association with Gingivitis
Gingivitis serves as a common precursor to both gingival recession and tooth mobility. The presence of gingivitis indicates the presence of harmful bacteria and inflammation in the gum tissue, which can lead to gum recession and eventual bone loss. Proper management of gingivitis through oral hygiene practices and regular dental visits is essential in preventing the progression of these conditions.
Preventing and Managing Gingival Recession and Tooth Mobility
Effective oral hygiene and regular dental care are vital for preventing and managing gingival recession and tooth mobility. Proper brushing and flossing techniques, along with professional cleanings and examinations, can help maintain healthy gums and minimize the risk of these conditions. Additionally, addressing risk factors such as smoking, teeth grinding, and poor oral habits can contribute to a healthier oral environment.
Conclusion
Understanding the connection between gingival recession and tooth mobility sheds light on the importance of proactive oral health care. By recognizing the impact of these conditions and their association with gingivitis, individuals can take steps to protect their gum and tooth health. Through consistent oral hygiene practices and regular visits to the dentist, it is possible to maintain healthy gums and minimize the risk of tooth mobility and associated complications.